Amazon Web Services
2006: Amazon launched Amazon Web Service (AWS) on a utility computing basis although the initial released dated back to July 2002.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a collection of remote computing services (also called web services) that together make up a cloud computing platform, offered over the Internet by Amazon.com.
The most central and well-known of these services are Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud )and Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service).
Book:
Amazon Web Services is based on SOA standards, including HTTP, REST, and SOAP transfer protocols, open source and commercial operating systems, application servers, and browser-based access.
Topics:
1. Amazon CloudWatch
2. AWS CloudFormation
3. AWS CloudTrail
4. AWS Command Line Interface
5. AWS Config
6. AWS Management Console
7. AWS OpsWorks
8. AWS Service Catalog
9. Trusted Advisor
10. AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell
1). Amazon CloudWatch
· Amazon CloudWatch monitors your AWS resources and applications you run on AWS in real-time.
· Amazon CloudWatch is a web service that enables you to collect, view, and analyze Metrics.
· Amazon CloudWatch is basically a Metrics Repository. An AWS product—such as Amazon EC2—puts metrics into the repository, and you retrieve statistics based on those metrics.
· You can use metrics to collect and track metrics to:
o To calculate statistics and then present the data graphically in the CloudWatch console.
o Create alarms that initiate Auto Scaling and Amazon SNS actions on your behalf.
o Gain system-wide visibility into Resource Utilization, Application Performance, and Operational Health.
o Configure alarm actions to stop, start, or terminate an Amazon EC2 instance when certain criteria are met. For example, you can monitor the CPU usage and Disk Reads and writes of your Amazon EC2 instances and then use this data to determine whether you should launch additional instances to handle increased load. You can also use this data to stop under-used instances to save money.

Amazon CloudWatch Events
· Use them to deliver a timely stream of system events that describe changes in AWS resources to AWS Lambda functions, streams in Amazon Kinesis Streams, Amazon SNS topics, or built-in targets.
· Using simple rules that you can set up quickly, you can match events and route them to one or more target functions or streams.
· CloudWatch Events becomes aware of operational changes as they happen and takes action, sending messages to respond to the environment and activating functions, making changes, capturing state information, and taking corrective action
Amazon CloudWatch Logs
· You can use this to monitor, store, and access your log files from Amazon EC2 instances, AWS CloudTrail, or other sources.
· You can then retrieve the associated log data from CloudWatch Logs using the Amazon CloudWatch console, the CloudWatch Logs commands in the AWS CLI, the CloudWatch Logs API, or the CloudWatch Logs SDK.
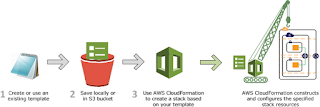
2). AWS CloudFormation
· AWS CloudFormation enables you to create and provision AWS infrastructure deployments predictably and repeatedly.
· It helps you leverage AWS products such as Amazon EC2, Amazon Elastic Block Store, Amazon SNS, Elastic Load Balancing, and Auto Scaling to build highly reliable, highly scalable, cost-effective applications in the cloud without worrying about creating and configuring the underlying AWS infrastructure. AWS CloudFormation enables you to use a template file to create and delete a collection of resources together as a single unit (a stack).
· AWS CloudFormation is a service that helps you Model and Set up your AWS resources so that you can spend less time managing those resources and more time focusing on your applications that run in AWS.
· You create a template that describes all the AWS resources that you want (like Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon RDS DB instances), and AWS CloudFormation takes care of provisioning and configuring those resources for you. You don't need to individually create and configure AWS resources and figure out what's dependent on what; AWS CloudFormation handles all of that.
AWS CloudFormation Concepts
· Templates
· Stacks
When you use AWS CloudFormation, you work with templates and stacks.
You create templates to describe your AWS resources and their properties.
Whenever you create a stack, AWS CloudFormation provisions the resources that are described in your template.
Templates
· An AWS CloudFormation template is a text file whose format complies with the JSON standard. You can save these files with any extension, such as .json, .template, or .txt.
· AWS CloudFormation uses these templates as blueprints for building your AWS resources. For example, in a template, you can describe an Amazon EC2 instance, such as the instance type, the AMI ID, block device mappings, and its Amazon EC2 key pair name.
· Whenever you create a stack, you also specify a template that AWS CloudFormation uses to create whatever you described in the template.
Stacks
· When you use AWS CloudFormation, you manage related resources as a single unit called a stack. In other words, you create, update, and delete a collection of resources by creating, updating, and deleting stacks.
· All the resources in a stack are defined by the stack's AWS CloudFormation template.
· Suppose you created a template that includes an Auto Scaling group, Elastic Load Balancing load balancer, and an Amazon RDS database instance. To create those resources, you create a stack by submitting the template that you created, and AWS CloudFormation provisions all those resources for you. To update resources, you first modify the original stack template and then update your stack by submitting the modified template.
· 
3). Amazon CloudTrail
· With AWS CloudTrail, you can monitor your AWS deployments in the cloud by getting a history of AWS API calls for your account.
· This includes API calls made via the AWS Management Console, the AWS SDKs, the command line tools, and higher-level AWS services.
· You can also identify which users and accounts called AWS APIs for services that support CloudTrail, the source IP address the calls were made from, and when the calls occurred.
· You can integrate CloudTrail into applications using the API, automate trail creation for your organization, check the status of your trails, and control how administrators turn CloudTrail logging on and off.
How it works:
· AWS CloudTrail captures AWS API calls and delivers log files to an Amazon S3 bucket that you specify.
· Optionally, you can configure AWS CloudTrail to deliver events to a log group to be monitored by CloudWatch Logs.
· You can also choose to receive Amazon SNS notifications each time a log file is delivered to your bucket.
· You can create two types of trails:
o A trail that applies to all regions (Default)
o A trail that applies to one region
By default, your log files are encrypted using Amazon S3 Server-Side Encryption (SSE).You can store your log files in your bucket for as long as you want, but you can also define Amazon S3 lifecycle rules to archive or delete log files automatically. CloudTrail typically delivers log files within 15 minutes of an API call. In addition, the service publishes new log files multiple times an hour, usually about every five minutes. These log files contain API calls from all of the account's services that support CloudTrail.
4). Amazon Command Line Interface
· AWS CLI is a unified tool that provides a consistent interface for interacting with all parts of AWS.
· AWS CLI commands for different services are covered in the accompanying user guide, including descriptions, syntax, and usage examples.
5). AWS Config Documentation
· AWS Config provides a Detailed View of the Configuration of AWS resources in your AWS account.
· This inlcudes
o How they are configured,
o How they are related to one another, and
o How the configurations and their relationships have changed over time.
· AWS Config supports the following AWS resources
o Amazon EBS
o Amazon EC2
o Amazon VPC
o AWS CloudTrail
o AWS Identity and Access Management
· With AWS Config, you can do the following:
o Evaluate your AWS resource configurations for desired settings.
o Get a snapshot of the current configurations of the supported resources that are associated with your AWS account.
o Retrieve configurations of one or more resources that exist in your account.
o Retrieve historical configurations of one or more resources.
o Receive a notification whenever a resource is created, modified, or deleted.
o View relationships between resources. For example, you might want to find all resources that use a particular security group.
6). AWS Management Console
· The AWS Management Console is a Web Application for managing Amazon Web Services.
· The console provides an intuitive user interface for performing many AWS tasks, such as working with Amazon S3 buckets, launching and connecting to Amazon EC2 instances, setting Amazon CloudWatch alarms, and so on.
· Each service has its own console, which you can access from the AWS Management Console. The console also provides information about your account and about billing.
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/awsconsolehelpdocs/latest/gsg/getting-started.html
7). AWS OpsWorks
· AWS OpsWorks provides a simple and flexible way to create and manage Stacks and Applications.
· With AWS OpsWorks, you can provision AWS resources, manage their configuration, deploy applications to those resources, and monitor their health.
Cloud-based computing usually involves groups of AWS resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon RDS instances, which must be created and managed collectively. For example, a web application typically requires application servers, database servers, load balancers, and so on. This Group Of Instances is typically called a Stack; a simple application server stack might look something like the following.
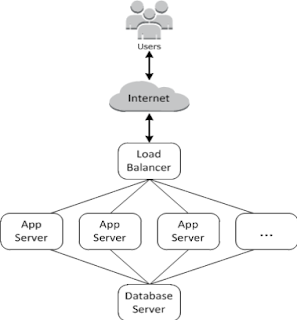
In addition to creating the instances and installing the necessary packages, you typically need a way to distribute applications to the application servers, monitor the stack's performance, manage security and permissions, and so on.
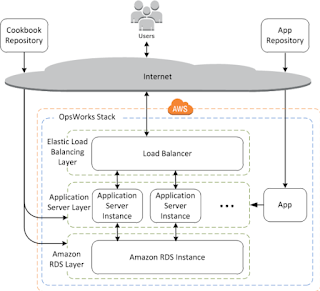
AWS OpsWorks provides a simple and flexible way to create and manage stacks and applications. Here's how a basic application server stack might look with AWS OpsWorks. It consists of a group of application servers running behind an Elastic Load Balancing load balancer, with a backend Amazon RDS database server.
8). AWS Service Catalog
· AWS Service Catalog allows IT administrators to Create, Manage, And Distribute Portfolios Of Approved Products to end users, who can then access the products they need in a personalized portal.
· Typical products include servers, databases, websites, or applications that are deployed using AWS resources (for example, an Amazon EC2 instance or an Amazon RDS database). You can control which users have access to specific products to enforce compliance with organizational business standards, manage product lifecycles, and help users find and launch products with confidence.
· AWS Service Catalog allows organizations to Create And Manage Catalogs of IT services that are approved for use on AWS.
· These IT services can include everything from virtual machine images, servers, software, and databases to complete multi-tier application architectures.
· AWS Service Catalog allows organizations to Centrally Manage Commonly Deployed IT services, and helps organizations achieve consistent governance and meet compliance requirements, while enabling users to quickly deploy only the approved IT services they need.
9). AWS Support Documentation
· AWS Support provides support for users of Amazon Web Services. All users have access to account and billing help in the AWS Support Center.
· In addition, customers with some support plans have access to additional features, including AWS Trusted Advisor and an API for programmatic access to support cases and Trusted Advisor.
· AWS Support is a one-on-one, Fast-Response Support Channel that is staffed with experienced support engineers.
· The service helps customers get the most from the products and features provided by Amazon Web Services.
· There are four levels, or tiers, of AWS Support:
o Basic - Free
o Developer,
o Business, and
o Enterprise.
· The Basic tier is free of charge and offers support for account and billing questions and service limit increases.
· The other tiers offer an unlimited number of technical support cases with pay-by-the-month pricing and no long-term contracts, providing developers and businesses flexibility to choose the level of support that meets their needs.
10). AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell Documentation
· The AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell are a set of PowerShell cmdlets that are built on top of the functionality exposed by the AWS SDK for .NET.
· The Tools enable you to script operations on your AWS resources from the PowerShell command line.
· Although the cmdlets are implemented using the service clients and methods from the SDK, the cmdlets provide an idiomatic PowerShell experience for specifying parameters and handling results.
· For example, the cmdlets for the PowerShell Tools support PowerShell pipelining—that is, you can pipeline PowerShell objects both into and out of the cmdlets.
Regards,
Arun Manglick